12 characteristics and 6 recommendations on CSR Reporting in China 2020
2020-12-21GoldenBeeGoldenBee0

The 2020 GoldenBee Research on CSR Reporting in China 2020 was released on December 3 in Beijing, during the 13th International Conference on CSR Reporting in China.
Guan Zhusun, Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer of GoldenBee Consulting made a speech themed “GoldenBee Research on Corporate Social Responsibility Reporting in 2020”. He explained and analyzed the general trend of China's CSR Reporting in 2020, and put forward six recommendation for the development of CSR Reports in China.
According to Mr. Guan, a high-quality CSR report should follow the GoldenBee "Triple-A Report" model, which is summarized through longtime attention, collection and evaluation of the overall situation of CSR reports in China.
First, an A-level report should be able to present the underlying information completely.
Second, the core content of an A-level report is a good response to the concerns of stakeholders.
Third, an A-level report should be able to follow the basic principles, including readability, credibility, comparability and innovativeness.
A high-quality CSR report is excellent in its completeness, materiality, readability, credibility, comparability and innovativeness. The six aspects are not of same proportion in the report assessment, for example, materiality weighs the most. If the stakeholders' concerns could be well responded to, meanwhile the most important content on sustainable business development can be presented in the report, the report is at least half successful, and plus complete information, basic norms, the report should be a high-quality CSR report.
Regarding this year's CSR reports released in China, five trends are presented:
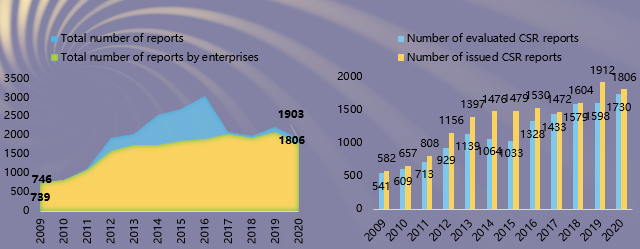
First, the number of reports grew rapidly from 2011 to 2016. Over the last three years, the number has stabilized. From January 1 to October 31, 2020, 1,903 CSR reports were collected, of which 97 were from non-business organizations and 1,806 were from enterprises.
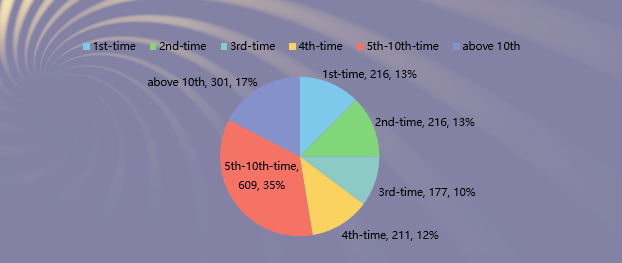
Second, the largest number of reports were issued at the 5th-10th times, accounting for 35.20%, lower than in 2019. The proportion of first-time issued reports was 12.49%, slightly higher than in 2019.
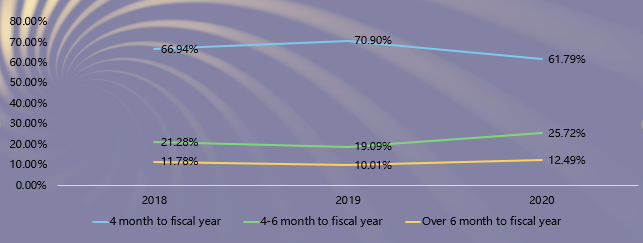
Third, the largest number of reports was issued within four months to the fiscal year, accounting for 61.79%, down from 70.90% in 2019. Affected by COVID-19, some enterprises (including listed companies) delayed the release of their reports.
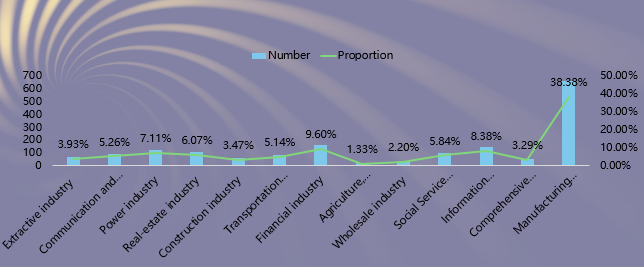
Fourth, manufacturing industry issued the largest number of reports, accounting for 38.38%, decreasing slightly from the year 2019 and 2018, followed by financial, information technology, power and real estate industries, accounting for 9.60%, 8.38%, 7.11% and 6.07%, respectively.
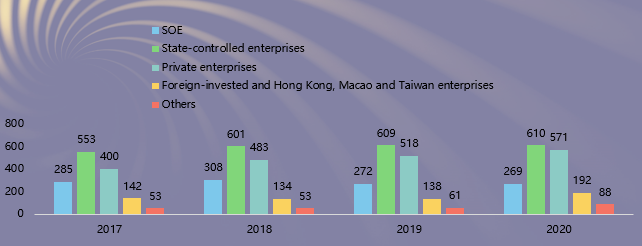
Fifth, there are 879 state-owned and state-controlled enterprises in the research, accounting for 50.81%, 571 private enterprises for 33.01%, and 192 foreign-invested and Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan enterprises for 11.10%.
2020年中国CSR报告呈现12个特征
After analyzing more than 1,800 reports, the following features are revealed:
Characteristics 1: The quality of China's CSR reports during the “13th Five-Year Plan” period is stable, with the comprehensive index remaining at the level of 1,300 points. The report quality and the number of excellent reports in the last three years are basically balanced.

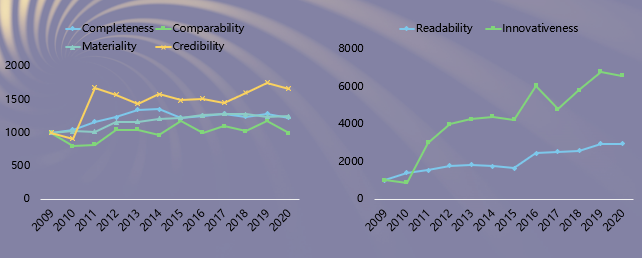
Characteristics 2: The levels of report completeness, materility and readability are relatively high, and has improved a bit on the former high basis, of which readability has increased significantly. Credibility, innovativeness and comparability are at relatively low levels; compared with the base period, innovativeness has increased significantly, and credibility has been greatly improved.
Characteristics 3: The reports generally lack the disclosure of the materiality management, mainly reflected in the leadership of the top governance bodies of material topics, as well as the objectives, plans, processes and outcomes of materiality management.
1. Less than one-third of enterprises disclose the CSR management structure and the participation of top leadership in CSR management, and fewer reports combine the concept of social responsibility with the development strategy.
2. The overall management of material topics in the reports remains at the stage of explaining the material reasons, lacking further explanation of how enterprises manage material topics systematically.
3. The proportion of reports on the disclosure of management approaches and evaluation systems has been further reduced, and the level of information disclosure on CSR materiality management and evaluation is weak.
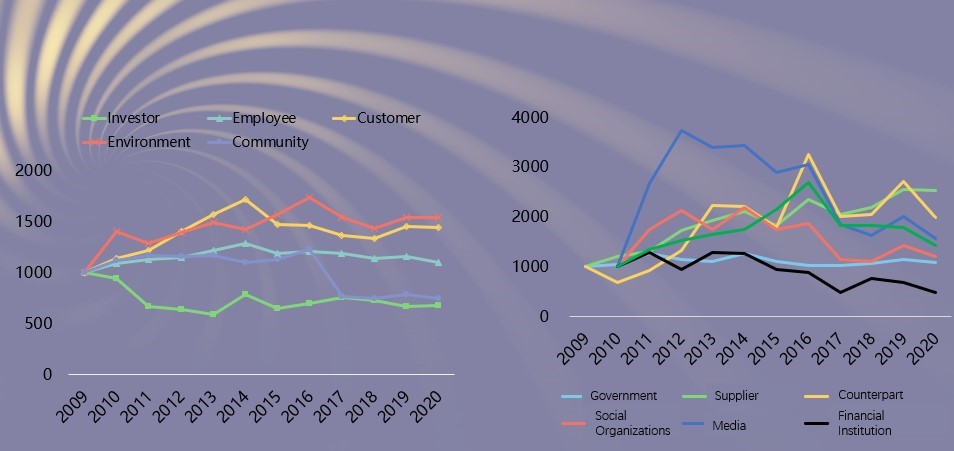
Characteristics 4: Compared with the base period, enterprises pay greater attention to the information disclosure of stakeholders such as the environment, customers, suppliers, industry counterparts, media and others. The reports have a relatively high degree of information disclosure of key social responsibility topics including protection of customers’ privacy, pollution and emission reduction, community volunteering activities, educational support and disaster relief donation.
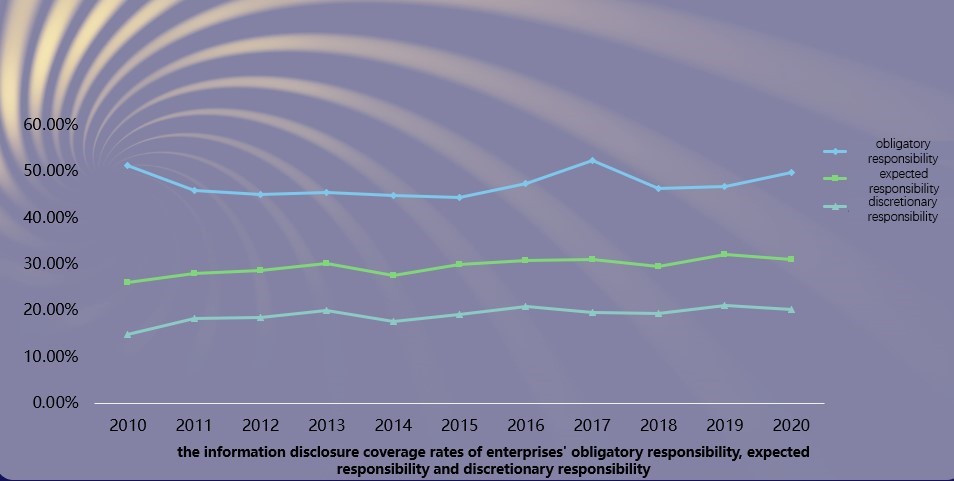
Characteristics 5: Since 2009, the information disclosure coverage rates of enterprises' obligatory responsibility, expected responsibility and discretionary responsibility account for around 50%, 30% and 20% respectively. This reflects that the current CSR information disclosure in China is overall in the development stage, as the majority only seeks to comply with laws and regulations.
Characteristics 6: Compared with the base period, social responsibility reporting index of each industry shows an upward trend, with the quality of the reports from storage and transport and real estate seeing the most significant increase.
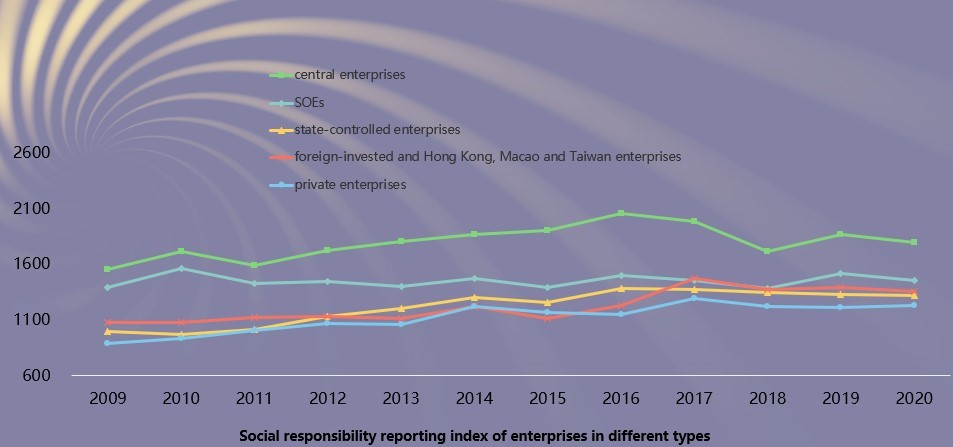
Characteristics 7: The reports of central SOEs have maintained leading quality. The report quality of state-controlled enterprises, foreign-invested and Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan enterprises, and private enterprises increased steadily.
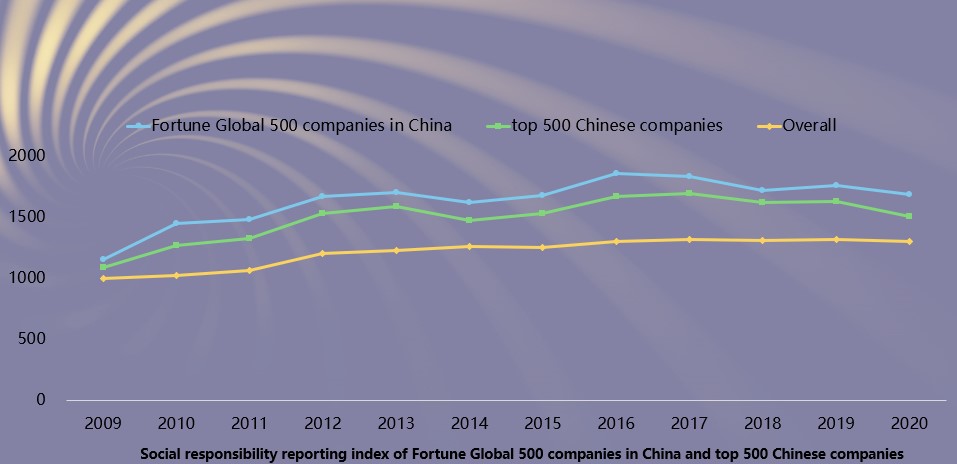
Characteristics 8: The report quality and the report quality improvement speed of Fortune Global 500 companies in China and top 500 Chinese companies are significantly higher than the average CSR reporting level in China. More than 40% of top 500 Chinese companies have never issued a social responsibility report.
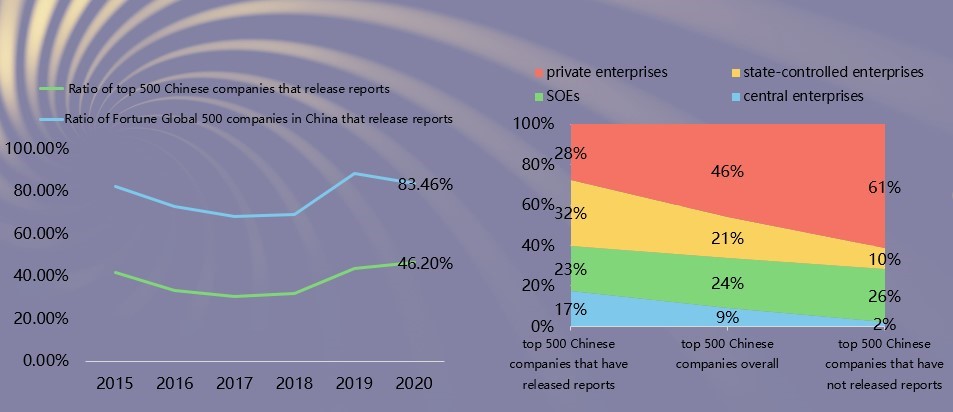
Characteristics 9: Quality gaps between reports from different industries, ownership and size are narrowing. The quality of reports with low grades is catching up.
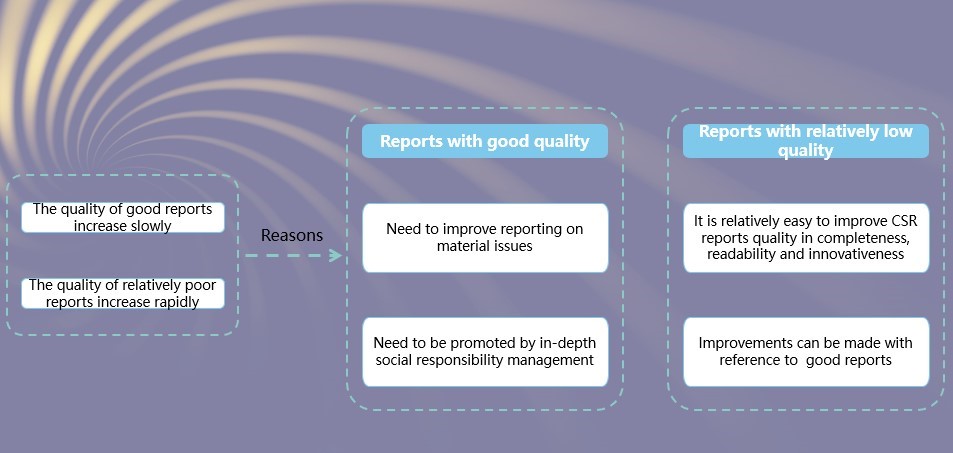
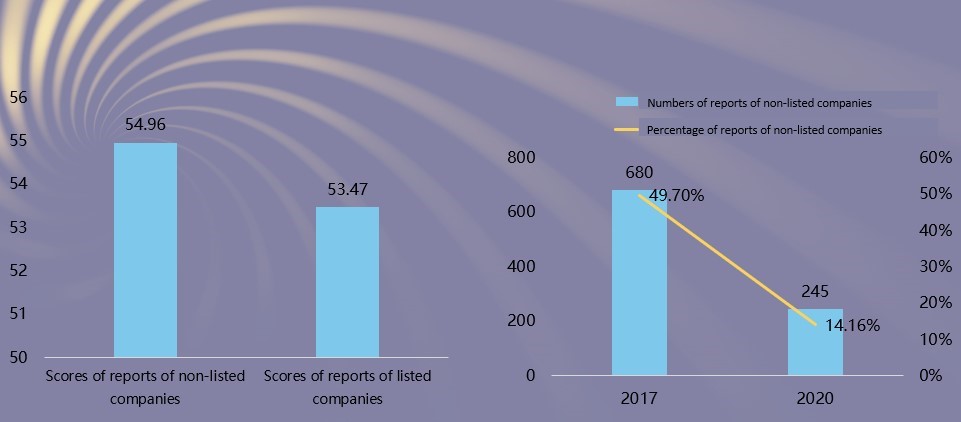
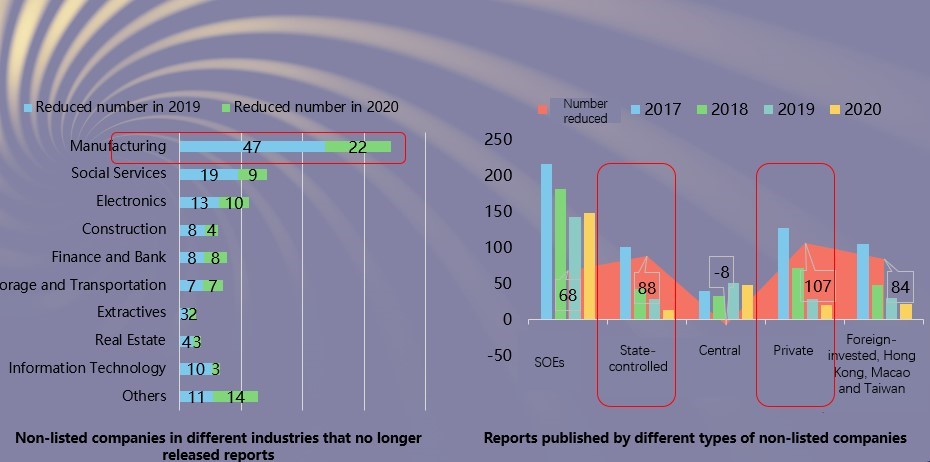
Characteristics 10: The quality of the reports issued by non-listed companies is higher than that of listed companies but the number and proportion of reports issued by non-listed companies show a significant downward trend. Among non-listed companies, the number of reports from manufacturing, private and state-controlled companies decreased significantly.
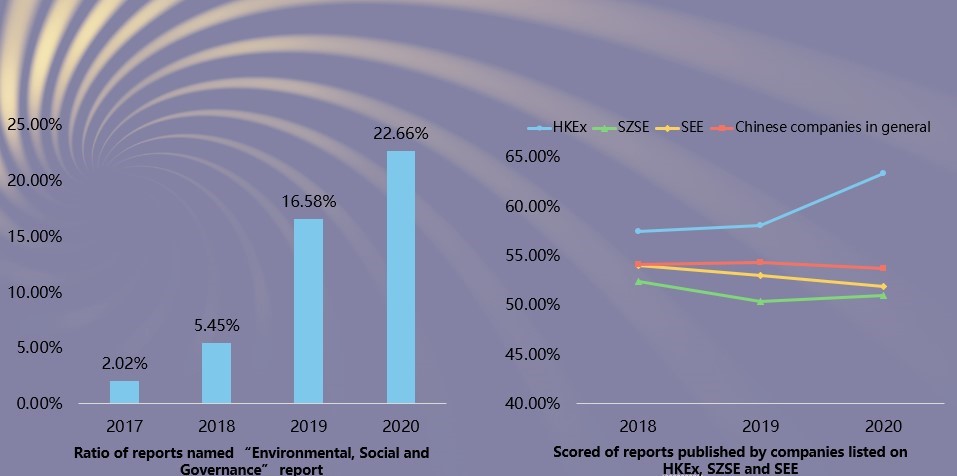
Characteristics 11: Enterprises in Chinese mainland listed on Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited (HKEx) have better performance in terms of CSR reporting than those listed on Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) and Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
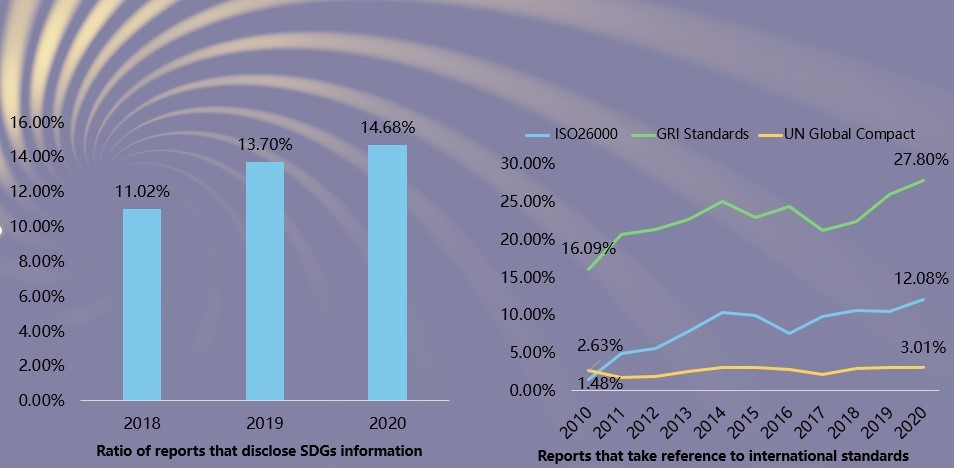
Characteristics 12: The level of internalization of CSR reporting in China has increased significantly.
Based on above analysis, we put forward six recommendations to support enterprises in China to improve their CSR reporting.
1. Enhance the transparency of operation and elevate the level of social responsibility information disclosure during the 14th Five-Year Plan period, and thus to strengthen the strategic understanding of CSR information disclosure.
2. Strengthen disclosure of materiality management progress from the perspectives of management goals, plans, processes and results, and thus to improve the management of the reports.
3. Reflect enterprises’progress in CSR index system building and quantitative management by CSR disclosure, to improve CSR management, and thus to enhance the comparability of the reports.
4. Attach more attention to issues including pollution prevention, biodiversity and ecosystem protection, greenhouse gas management, employees’ health and safety and career development as well as suppliers’ social responsibility levels, and thus to enhance the materiality of the reports.
5. Strengthen the guidance and regulation for CSR disclosure of
enterprises listed on Shanghai Stock Exchange and Shenzhen Stock Exchange to improve their ESG disclosure quality, and thus to improve the standardization of reports.
6. Strengthen CSR disclosure of top 500 Chinese companies and raise awareness about the importance of CSR disclosure.
Best Practices
- The 100-year brand — Air Liquide also has a sense of juvenile
- Beijing Public Transportation Corporation: Developing green transportation to build a harmonious and livable capital
- CGN: Building a modern factory in barren deserts and developing a new win-win cooperation model along “Belt and Road”
Upcoming Event

All the materials on the site “Source: XXX (not from this site)” have been reprinted from other media. They do not imply the agreement by the site.
All the materials with “Source: CSR-China Website” are the copyright of CSR-China Website. None of them may be used in any form or by any means without permission from CSR-China Website.
GoldenBee Official WeChat
Copyright © Csr-china.net All Right Reserved.
京ICP备19010813号










