Highlight | GoldenBee Research on CSR Reporting in China 2019
2019-12-17GoldenBeeGoldenBee0

“How to identify whether a CSR report is of high quality? We believe that excellent basic information disclosure, excellent response to core content, and excellent compliance with basic principles are the bases for high-quality CSR reporting.”
Said Mr. Yin Gefei, Founder and Chief Expert of GoldenBee, on the 12th International Conference on CSR Reporting in China held on December 5.Mr. Yin further explained that excellent basic information disclosure means that companies should proactively express their views on social responsibility and sustainable development, and their corresponding plans to welcome opportunities and handle risks; excellent response to core content means that companies should disclose their key information about CSR performance; excellent compliance with basic principles means that CSR reports should be measured from the four aspects of credibility, readability, comparability, and innovativeness.
The above statement is not only a response to questions of readers of the series of articles about the forum published by GoldenBee through the WeChat official account but also introduces the highlight of the forum - the official release of the GoldenBee Index on Corporate Social Responsibility Reporting in China 2019.
To respond to the concerns of domestic practitioners and researchers from CSR-related fields about the CSR reporting, Mr. Yin Gefei said that studies through more than ten years show that the quality of CSR reports in China has a gradual increase. “Compared with 2009, the innovativeness, readability, and credibility of CSR reports have improved relatively fast, while the comparability, materiality, and completeness have shown slower improvement.” Yin Gefei said.
In addition, Mr. Yin Gefei shared the main findings and recommendations about CSR reporting in China in 2019, which have been sorted out by the editor and presented below to share with all readers.
CSR reporting performance in China
From 2001 to 2019, the number of social responsibility reports released by enterprises in China has been increasing, and the increase has been picking up since 2011. From January 1 to October 31, 2019, a total of 1,993 social responsibility reports were released, among which 1,912 were released by business organizations, accounting for 95.9% of the total. Non-business organizations released 81 reports, accounting for 4.1% of the total. A total of 671 enterprises published their 5th to 10th CSR report during the period, accounting for 41.99% of the total, and 197 enterprises published their first CSR report. Annual CSR reports accounted for 98.62% of the total, and only 22 were non-annual reports.
More than 60% of the reports have 30 pages or more, and reports less than 30 pages account for only 38.61% of the total. In the past three years, the number of reports released within four months after the end of the fiscal year has increased steadily, and the increase rate reached 8.1% compared to the year 2017. The reporting enterprises are mainly from industries of manufacturing, financial and insurance, power, coal, water and gas production and supply, information technology (IT), real estate, social services, etc.
Enterprises from eastern China released 1,112 reports, accounting for 69.59% of the total; Beijing, Shanghai, Guangdong, and Zhejiang were ranked among the top four provinces and municipalities in terms of the number of CSR reports released for the third consecutive year. Among the reporting enterprises, 881 are state-owned or state-holding companies, accounting for 55.13% of the total; 1,262 are growing companies, accounting for 78.97% of the total; 336 are leading enterprises, accounting for 21.03% of the total.“
Social Responsibility Report” was included in the titles of 76.16% of the reports; TheSustainability Reporting Guidelines of Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) was the document referred to most frequently by the reports; 22.65% of the reports referred to ISO 26000 or GB/T 36001. 52% of the reports provided feedback channels; 93.41% of the reports had electronic versions. There were 54 national reports, accounting for 3.38% of the total; 5.19% of the reports were subject to third-party verification; the vast majority of the reports were independently released, and only 17 reports were attached to the annual report or formed specific chapters of the annual report.
Our findings
➤Characteristics 1: The overall quality of reports has shown a stepwise upward trend since 2009. Since the launch of the 13th Five-Year Plan, the comprehensive index of reports has been maintained at around 1,300. In 2019, the quality of the reports increased slightly, and the proportion of reports in “good” rating and above increased year on year.
Said Mr. Yin Gefei, Founder and Chief Expert of GoldenBee, on the 12th International Conference on CSR Reporting in China held on December 5.Mr. Yin further explained that excellent basic information disclosure means that companies should proactively express their views on social responsibility and sustainable development, and their corresponding plans to welcome opportunities and handle risks; excellent response to core content means that companies should disclose their key information about CSR performance; excellent compliance with basic principles means that CSR reports should be measured from the four aspects of credibility, readability, comparability, and innovativeness.
The above statement is not only a response to questions of readers of the series of articles about the forum published by GoldenBee through the WeChat official account but also introduces the highlight of the forum - the official release of the GoldenBee Index on Corporate Social Responsibility Reporting in China 2019.
To respond to the concerns of domestic practitioners and researchers from CSR-related fields about the CSR reporting, Mr. Yin Gefei said that studies through more than ten years show that the quality of CSR reports in China has a gradual increase. “Compared with 2009, the innovativeness, readability, and credibility of CSR reports have improved relatively fast, while the comparability, materiality, and completeness have shown slower improvement.” Yin Gefei said.
In addition, Mr. Yin Gefei shared the main findings and recommendations about CSR reporting in China in 2019, which have been sorted out by the editor and presented below to share with all readers.
CSR reporting performance in China
From 2001 to 2019, the number of social responsibility reports released by enterprises in China has been increasing, and the increase has been picking up since 2011. From January 1 to October 31, 2019, a total of 1,993 social responsibility reports were released, among which 1,912 were released by business organizations, accounting for 95.9% of the total. Non-business organizations released 81 reports, accounting for 4.1% of the total. A total of 671 enterprises published their 5th to 10th CSR report during the period, accounting for 41.99% of the total, and 197 enterprises published their first CSR report. Annual CSR reports accounted for 98.62% of the total, and only 22 were non-annual reports.
More than 60% of the reports have 30 pages or more, and reports less than 30 pages account for only 38.61% of the total. In the past three years, the number of reports released within four months after the end of the fiscal year has increased steadily, and the increase rate reached 8.1% compared to the year 2017. The reporting enterprises are mainly from industries of manufacturing, financial and insurance, power, coal, water and gas production and supply, information technology (IT), real estate, social services, etc.
Enterprises from eastern China released 1,112 reports, accounting for 69.59% of the total; Beijing, Shanghai, Guangdong, and Zhejiang were ranked among the top four provinces and municipalities in terms of the number of CSR reports released for the third consecutive year. Among the reporting enterprises, 881 are state-owned or state-holding companies, accounting for 55.13% of the total; 1,262 are growing companies, accounting for 78.97% of the total; 336 are leading enterprises, accounting for 21.03% of the total.“
Social Responsibility Report” was included in the titles of 76.16% of the reports; TheSustainability Reporting Guidelines of Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) was the document referred to most frequently by the reports; 22.65% of the reports referred to ISO 26000 or GB/T 36001. 52% of the reports provided feedback channels; 93.41% of the reports had electronic versions. There were 54 national reports, accounting for 3.38% of the total; 5.19% of the reports were subject to third-party verification; the vast majority of the reports were independently released, and only 17 reports were attached to the annual report or formed specific chapters of the annual report.
Our findings
➤Characteristics 1: The overall quality of reports has shown a stepwise upward trend since 2009. Since the launch of the 13th Five-Year Plan, the comprehensive index of reports has been maintained at around 1,300. In 2019, the quality of the reports increased slightly, and the proportion of reports in “good” rating and above increased year on year.

➤Characteristics 2: Compared with the base period, innovativeness, readability, and credibility of CSR reports have improved significantly, and materiality, comparability, and completeness have improved at a slower pace. In 2019, the credibility and comparability have improved significantly, and the materiality has decreased slightly.
➤Characteristics 3: Enterprises pay greater attention to information disclosure related to the management of CSR fulfillment of suppliers, pollution and emission reduction, protection of customers’ privacy, etc. Compared with the base period, the reports disclose a much larger amount of information related to industry counterparts, suppliers, and media.
➤Characteristics 4: The information disclosure of enterprises’ obligatory responsibility shows a decreasing trend, whereas that of expected responsibility, and discretionary responsibility presents an increasing trend. In 2019, enterprises’ information disclosure of obligatory responsibility, expected responsibility and discretionary responsibility increased slightly. Enterprises attach more significance to proactive and interactive information disclosure.
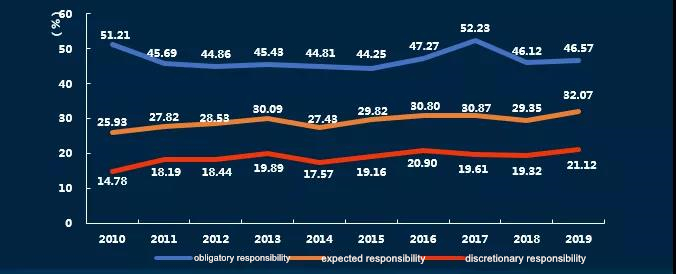
➤Characteristics 5: Compared with the base period, the overall quality of the reports of enterprises from storage and transport as well as mining industries are relatively high, and that of enterprises from industries of construction, power, coal, water and gas production and supply, information technology (IT), financial and insurance, and real estate is around the average level in China.
➤Characteristics 6: The reports pay more attention to information disclosure of social responsibility management, and attach great importance to information disclosure of social responsibility systems and management structures. Enterprises strengthen the analysis of risks and opportunities, identify and prioritize stakeholders, but need to improve information disclosure of social responsibility philosophy and performance.
➤Characteristics 7: The reports of central SOEs have maintained leading quality. The reports quality of private enterprises, foreign-invested and Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan enterprises show significant improvement compared with the base period. The reports of central SOEs have leading information disclosure in terms of the environment, community, counterparts, and social organizations, and the reports of foreign-invested and Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan enterprises have leading information disclosure in terms of customers and suppliers.
➤Characteristics 8: The number of reports released by Fortune Global 500 companies in China and top 500 Chinese companies has returned to a high point, and the quality of their reports is significantly higher than the average CSR reporting level of Chinese companies. There is still much room for improvement in the number and quality of reports released by top 500 Chinese companies.
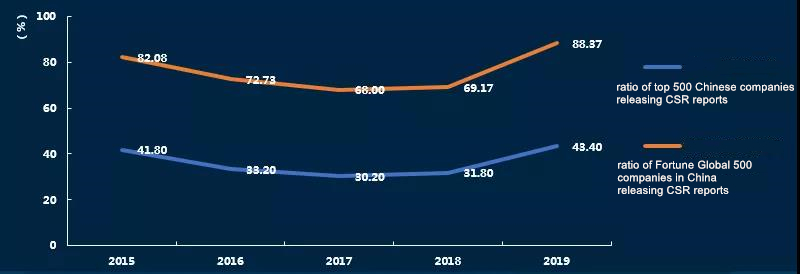
➤Characteristics 9: Listed companies are the main forces in CSR reporting, and the quality of CSR reports of non-listed companies is significantly higher than that of listed companies. Enterprises in Mainland China listed on Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited (HKEx) have better performance in terms of CSR reporting than those listed on Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) and Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
➤Characteristics 10: The number of reports that are compiled in accordance with international standards and have been increasing over the years, and the number of English reports has increased significantly. Enterprises attach more attention to responding to sustainable issues such as the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and its Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), climate change, and other sustainability issues.
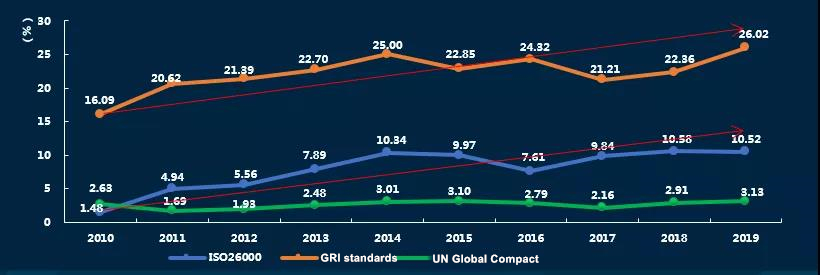
Our suggestions
Suggestion 1: Create a suitable system and environment to help top 500 Chinese companies realize the completeness of CSR reporting.
Suggestion 2: Strengthen the guidance for social responsibility information disclosure to motivate listed companies to improve the quality and standardization of social responsibility reporting.
Suggestion 3: Establish a market mechanism that encourages enterprises to disclose high-quality social responsibility information and form a virtuous cycle between market feedback and CSR fulfillment to strengthen the effect of feedback.
Suggestion 4: Strengthen the identification and comprehensive disclosure of key social responsibility topics to make the reports present CSR progress of enterprises in a more systematic and effective way, and thus enhance the materiality of the reports.
Suggestion 5: Enhance the engagement of stakeholders and independent third parties in the compilation of the report to avoid selective disclosure, and thus improve the credibilityof the reports.
Suggestion 6: Compare CSR performance of different enterprises to help stakeholders understand enterprises’ CSR performance in a more comprehensive manner, and thus enhance the comparability of the reports.
Suggestion 7: Strengthen information disclosure of CSR management and communicate enterprises’ progress during management progresses, including “planning-executing-inspecting-improving”, and thus improve the reports’ presentation of management-related topics.
Suggestion 8: Give full play to the advantageous role of social responsibility reporting as an internationally “language” to promote cultural integration in overseas operations and enhance disclosure of international topics of the reports.
Best Practices
- The 100-year brand — Air Liquide also has a sense of juvenile
- Beijing Public Transportation Corporation: Developing green transportation to build a harmonious and livable capital
- CGN: Building a modern factory in barren deserts and developing a new win-win cooperation model along “Belt and Road”
Upcoming Event

All the materials on the site “Source: XXX (not from this site)” have been reprinted from other media. They do not imply the agreement by the site.
All the materials with “Source: CSR-China Website” are the copyright of CSR-China Website. None of them may be used in any form or by any means without permission from CSR-China Website.
GoldenBee Official WeChat
Copyright © Csr-china.net All Right Reserved.
京ICP备19010813号










